Selection principles for submersible electric pumps
Release time:2019/3/26 14:15:58 AUTHOR:
Principles for selecting submersible electric pumps
Before purchasing a submersible pump, the appropriate submersible pump should be selected based on the specific usage conditions of the user, such as the required flow rate, head height, transformer configuration, water quality used, and usage environment, to ensure safety, reliability, and long-term use
Principle of selection
1) Select the base size of the electric pump (well diameter series) based on the diameter of the well (100mm, 150mm, 175mm, 200mm, 250mm, 300mm, 350mm, etc.), and then choose the specific specifications and models according to the actual flow rate and head of the well.
2) When lifting water in general clean water areas such as ponds, ditches, shallow wells, work surfaces, and sprinkler irrigation, QJB, WQK, and WQKD small submersible electric pumps can be preferred.
3) When transporting sewage containing solid particles and sewage pollutants, QW and SWQ submersible sewage pumps should be selected.
4) QJR series submersible electric pumps can be preferred for places with temperatures above 50 ℃ and slight corrosiveness, such as hot springs, geothermal deep wells, and winter heating.
Choose the Best Scope of Use
Submersible electric pumps of different specifications have different usage ranges. The standard values that the submersible electric pump should have under rated operating conditions as specified on the nameplate. As the flow rate and head change during use, the efficiency and output power of submersible electric pumps also change accordingly, which has a certain impact on the economy and reliability of submersible electric pump use. When the head is too low, the flow rate increases and the motor current increases, exceeding the rated current of the motor. Long term operation will burn out the motor; When using a submersible electric pump with a high head, the flow rate of the pump decreases, the efficiency decreases, and the axial force of the electric pump increases, which can easily cause motor wear. Therefore, when selecting and using a submersible electric pump, the appropriate range of use must be considered to ensure long-term reliable operation.
Three options for the base number of submersible electric pumps used in wells
Select the pump base number based on the existing wellbore diameter.
A submersible electric pump with a diameter of 200mm (8 ") can be selected for well use with a base size of 200QJ or below, such as the 200QJ, 175QJ, 150QJ, and 100QJ series.
For wells with a diameter of 250mm (10 "), submersible electric pumps with a capacity of 250QJ or less can be selected, such as the 250QJ, 200QJ, 175QJ series, etc.
When selecting, if the well depth exceeds 200m, the drilling data should be used and the verticality of the well should be considered. If the verticality of the well is not sufficient, a smaller series of submersible electric pumps should be selected, such as the 200QJ series for 250mm diameter, to prevent the electric pump from getting stuck and unable to go down.
Four options for flow rate of submersible electric pump
The flow rate of the water pump can be selected based on the optimal water inflow of the well. When selecting, the flow rate of the selected pump type should be determined based on the principle that the flow rate of the pump should be less than the maximum water inflow of the well. If the maximum water inflow of the well is 60 m3/h, the pump flow rate can be selected as 50 m3/h or 32 m3/h. Otherwise, if the selected pump flow rate is greater than the optimal water output of the well, the critical permeation velocity of the filter pipe (flower pipe) will be greater than the maximum allowable permeation velocity of the aquifer, which will cause sand particles in the aquifer to move, resulting in sedimentation of sediment flow in the well. In severe cases, it may cause the well to collapse and be scrapped.
Five options for the head of submersible electric pumps
Select the pump head based on the required lifting height and the overall loss of the pipeline system, given the selected pump flow rate. To ensure reliable pumping, the nameplate head of the selected submersible pump should be slightly higher than the actual required head.
H nameplate=(1.02-1.05) H actual
H actual=H net+H loss
In the formula, H is the actual vertical height difference m between the inlet and outlet water surfaces;
H loss: The sum of water head losses in the lifting pipeline, denoted as m. The loss of the lifting pipe is the sum of the loss along the way and the local loss.
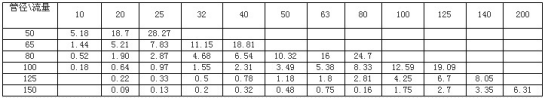
The loss per hundred meters of steel pipes of different specifications under different flow rates can be determined by the values in Table 1. From the table, it can be seen that for a certain specification of submersible pump, at rated flow rate, the thinner the lifting pipe, the greater the loss, the lower the lifting water, and the thicker the lifting pipe, the smaller the loss, and the higher the lifting water. Usually, the diameter of the lifting pipe is slightly larger or equal to that of the pump outlet to reduce pipeline losses.
The inlet of the submersible electric pump should be submerged 3m below the dynamic water level, and the lower end of the unit should be kept at a certain distance from the bottom of the well, greater than 3m. The length of the water lifting pipe can be determined based on the depth of the dynamic water level. Considering the fluctuation of the dynamic water level, the diving depth of the submersible pump inlet can be appropriately increased when determining the length of the lifting pipe. The diving depth of the unit below the net water level shall not exceed 70m. Example: There is a 10% well, and the specific information is as follows. Please purchase a submersible electric pump for this well. ① The diameter of the well is 200mm; ② The well surge rate is 60m3/h; ③ The vertical distance from the net water level in the well to the wellhead is 40m; ④ During the trial pumping, the net water level drops by 10 meters and stabilizes; ⑤ After the water is extracted from the well, it is transported to a sloping top with a gradient of 30 degrees and a slope length of 100m
Solution: H net=40+10+100 × sin30 °
Pipeline: 1=40+10+100=150 (m)
According to the table, it is more economical to use a 3 "pipeline when selecting a flow rate of 50m3/h.
The total loss of its pipeline: H loss=150 × 10.32%=15.48m
H Actual=100+15.48=115.48m H Ming=1.05 × 115.48m=121.254m
After using the manual for the submersible electric pump for well inspection, it is more reasonable to choose the 200QJ50-130-30 submersible electric pump for well use.
- PREV: Common troubleshooting solutions for water pumps
- NEXT: 没有了!








